Setting Up a Project
This tutorial will guide you through fundamental Synapse features for creating a project via the Synapse UI. You will learn how to:
Create your own project
Explore the project dashboard
Add a description to your project in the wiki
Share your work with other Synapse users, teams, or the public
Prerequisites
Anyone can browse public content on the Synapse website, but to create content using this tutorial, you will need to register for an account using your email address. You will receive an email message for verification to complete the registration process.
To upload files to Synapse, you will need to perform the additional step of becoming a certified user. Because Synapse stores data from human subjects research, Sage Bionetworks requires that you demonstrate understanding of privacy and security issues. You can complete your certification by taking a short certification quiz on Synapse.
Creating a Project
Projects are the main “containers” where information is stored and organized in Synapse. They are online workspaces where you can collaborate and share your work with teammates. Projects can be shared with individuals, small teams, or large consortia. Projects can be private so only you and your team can see what’s inside, or they can be shared publicly for anyone to browse.
To create a new project:
Click the Projects icon in the Synapse toolbar
Click the plus sign (+) next to Projects
Enter a unique name for your project and click Save
Synapse will automatically open your new project so you can view your project dashboard.
Exploring the Project Dashboard
Your project dashboard allows you to see the different elements of your project at once. At the top of the project page, you can click the star next to your project name to add it to a list of favorites.
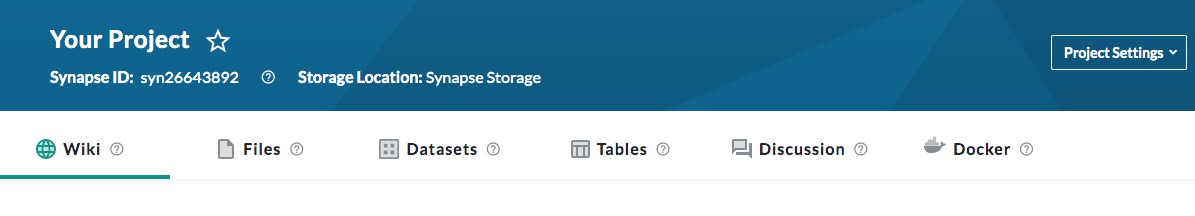
Below the project name, the Synapse ID (synID) is a unique number used to reference this project, and it is a powerful tool to identify and manage content. Projects, folders, files, tables, views, datasets, and wikis all have unique synIDs that can be used to navigate to and reference these specific items. The synID never changes and is always accessible in the URL and visible on the web. If you use one of the programmatic clients to interact with Synapse, you can use synIDs to create scripts that will work universally for anyone and without the need for specifying file paths.
The project dashboard also has tabs for different sections of your project:
Wiki: A wiki is like a virtual notebook where you can describe your research so others can understand your goals, methods, or anything else you want to communicate about your project.
![]() To learn more, see Wikis.
To learn more, see Wikis.
Files: This tab contains a directory of all of your files and folders within this project. Use this tab to see the hierarchy or structure of information as you add it.
![]() To learn more, see Uploading and Organizing Data Into Projects, Files, and Folders.
To learn more, see Uploading and Organizing Data Into Projects, Files, and Folders.
Datasets: This tab contains any datasets that you have created. A dataset is a collection of files that already exist in Synapse that may be hosted in one or more Synapse projects or folders.
![]() To learn more, see Datasets.
To learn more, see Datasets.
Tables: This tab contains tabular data. You can upload data tables or create them directly from the Synapse interface. You can also use this tab to create views, which are tables of other data in Synapse.
![]() To learn more about tables, see Organizing Data With Tables.
To learn more about tables, see Organizing Data With Tables.
![]() To learn more about views, see Views.
To learn more about views, see Views.
Discussion: Use this tab to communicate with teammates in a discussion forum.
![]() To learn more, see Discussion Forums.
To learn more, see Discussion Forums.
Docker: Docker is a platform for creating virtual containers to bundle code and other dependancies. You can add a Docker container to a project and share it with your teammates.
![]() To learn more, see Synapse Docker Registry.
To learn more, see Synapse Docker Registry.
Adding a Project Wiki
A wiki is a virtual document that can be edited by multiple people on the web. Wikis are powerful tools to add information about your project, and Synapse offers over a dozen widgets to customize your wiki pages. Use wikis to provide descriptions of your project goals, methods, and data.
Wiki pages can be written using text, Markdown, or basic HTML. Content can include images, tables, code blocks, LaTeX formatted equations, scholarly references, and references to other things in Synapse.
To add wiki content:
Click on the Wiki tab and use the Wiki Tools menu.
Choose Edit Wiki to add or edit wiki content.
From the editing window, click Preview to check your work. Click Save when you are finished.
![]() For more information on how to organize and customize your wiki content, see Creating and Managing Wikis.
For more information on how to organize and customize your wiki content, see Creating and Managing Wikis.
Sharing and Teams
By default, your project and anything inside it are private, so only you can see it. However, you can share an entire project with specific users, teams, or make it public so anyone can browse your content.
![]() For more information on how Synapse can help you control access to your data, see Sharing Settings, Permissions, and Conditions for Use.
For more information on how Synapse can help you control access to your data, see Sharing Settings, Permissions, and Conditions for Use.
To share a project:
Click on the Project Settings menu and select Project Sharing Settings.
Enter the usernames or team names to add collaborators.
To make the project publicly viewable, click Make public and then adjust the access levels for registered users and anyone on the web.
Groups of users can form Synapse teams for collaboration. Teams can be used for managing permissions and for communicating with your collaborators. Sharing something with a single team instead of many individual users can help administrators manage large, complex projects.
![]() Learn more about teams here
Learn more about teams here
![]() And learn about using teams to manage group communication and project permissions at Managing Data Access With Teams.
And learn about using teams to manage group communication and project permissions at Managing Data Access With Teams.
Anything inside your project will automatically inherit the same sharing settings as the project itself. In other words, if your project is public, then all of the contents within the project will also be public. If needed, you can change these settings so that certain files or folders are only shared with specific groups of users.
